A good guide comes from the United States Preventive Services Task Force, an independent panel of experts. Its recommendations help define high-quality preventive health care for Americans.
Screening tests are designed to detect hidden disease in otherwise healthy people. Which ones you should have aren’t set in stone—experts often disagree on when to start having screening tests, how often they should be performed, and when to stop.
Keep in mind that the benefits and risks of screening tests and procedures change as you get older. Your doctor can help you tailor the recommendations below based on your goals of care, personal and family health history, age, and life expectancy.
| Test | Recommendation |
| Blood pressure | Have your blood pressured at least every once every two years if it is in the healthy range (under 120/80) or once a year if it is above normal (between 120/80 and 139/89). |
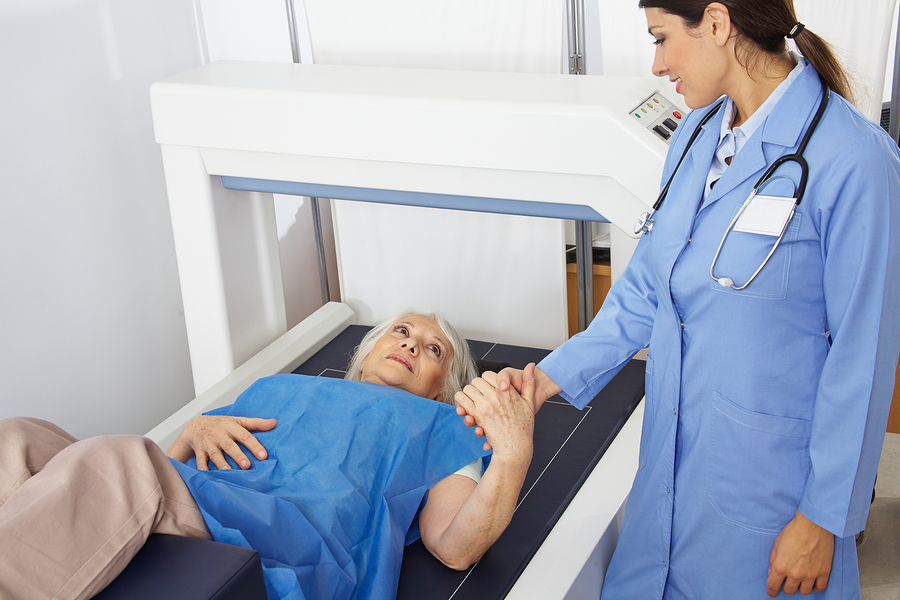
| Bone density | Get this test at least once at age 65 or after. Talk to your doctor or nurse about getting tested if you’re younger than 65 and about repeat testing. |
| Breast cancer | Mammography every two years for women ages 50-74. If you are 75 or older, ask your doctor or nurse if you need to continue having mammograms. |
| Cervical cancer | A Pap test is recommended every three years for women 21-65 who have a cervix. At age 30 a pap test and HPV test every 5 years is an option. If you are 65 or older, ask your doctor or nurse if you need to keep having Pap tests. |
| Colorectal cancer | Recommended for women ages 50-75. Talk to your doctor about which screening test, (fecal occult blood testing, sigmoidoscopy, or colonoscopy) or combination of tests, is best for you and how often you need it and if you should continue having these tests after 75. |
| Diabetes screening | Get tested for diabetes if your blood pressure is higher than 135/80 or if you take medicine for high blood pressure. |
| HIV/AIDS | Get tested for HIV/AIDS at least once after age 20, or earlier if you are at high risk for being infected by the human immunodeficiency virus. Discuss further testing with your doctor. |
| Lipid profile (total cholesterol, LDL, HDL, and triglycerides) | Starting at age 20, women at increased risk for developing heart disease should have regular cholesterol tests. |
| Lung cancer | Annual testing with low-dose computed tomography between ages 55 and 80 if you have smoked the equivalent of a pack a day for 30 years and currently smoke or have quit within the past 15 years. |
| Sexually transmitted infections (Chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis) | Get tested for chlamydia yearly through age 24 if you are sexually active or pregnant. After age 25, get tested for chlamydia and other sexually transmitted diseases if you are at increased risk for getting a sexually transmitted infection. |
Source:https://www.health.harvard.edu/womens-health
